Section 1: Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Section 2: The Evolution of AI: Focus on LLMs and Beyond
Section 3: The Advent of Multi-Modal AI
Section 4: Parallels with Historical Periods of Innovations
Section 5: AI and Its Economic Impact
Section 6: Future-Proofing Yourself Against AI Disruption
Section 7: How non AI-Native Organizations should Adapt
Section 8: Conclusion
In an era where technological advancement is not just a possibility but an inevitability, artificial intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront, heralding a new wave of innovation. This transformative force, akin to the seismic shifts brought about by the Agricultural, Industrial, and Digital Revolutions, is redefining the landscape of industries, employment, and economic development. In this deep dive, we explore the multifaceted world of AI, from its types and impact on various sectors to strategies for businesses and individuals to thrive in this AI-centric future.
Section 1: Understanding Artificial Intelligence
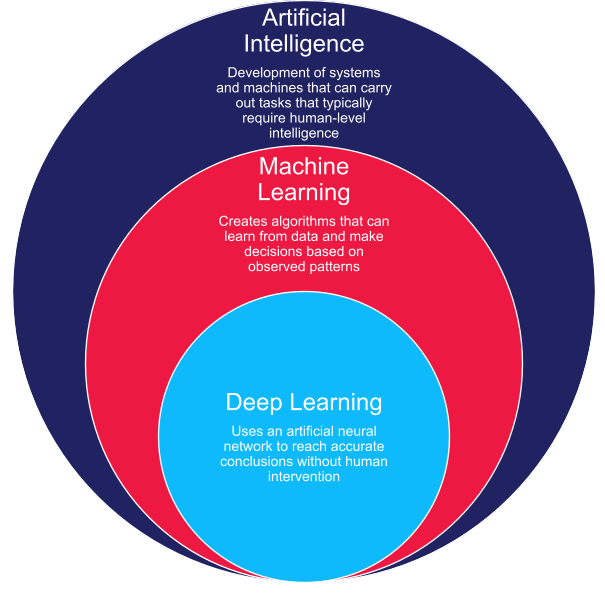
AI has evolved into a multifaceted field, encompassing a variety of forms and applications. Each of these forms, whether it be Large Language Models (LLMs), autonomous vehicle systems, or AI in healthcare, contributes uniquely to the AI landscape. To comprehend AI’s extensive reach, it’s instrumental to recognize its diverse forms and understand their categorization into four primary types: Narrow or Weak AI, General or Strong AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning.
Narrow or Weak AI encompasses AI systems designed for specific, well-defined tasks, lacking the versatility and self-awareness of human intelligence. Unlike General AI, which aims to perform a broad range of intellectual tasks, Narrow AI operates within a confined scope.
Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s ChatGPT series are prime examples of Narrow AI. These models, trained on extensive text datasets including over 300 billion words, excel in language tasks by predicting the next word in a sequence. However, their understanding is limited to identifying patterns in data; they don’t possess genuine comprehension. This limitation becomes apparent when they generate plausible but factually incorrect content, a result of processing text based on statistical probabilities, not actual understanding. Despite these shortcomings, ChatGPT 4, as an example, is revolutionizing how humans work and learn. A recent McKinsey analysis estimates that 30% of all total hours worked could be automated by 2030.
Other Narrow AI instances include facial recognition systems, chatbots, and recommendation engines. Each is proficient in its respective domain – identifying faces, conducting limited conversations, or suggesting products based on user history – but cannot extend its capabilities beyond its specific function. This specialization, while efficient, underscores the challenges in AI research to create systems with broader, more adaptable intelligence akin to humans.
General or Strong AI represents the aspirational pinnacle of artificial intelligence, where AI systems exhibit a broad, human-like understanding and cognitive abilities. Unlike Narrow AI, which is limited to specific tasks, General AI is characterized by its capacity to learn, reason, and apply intelligence across an extensive range of tasks and environments, mirroring human intellectual capabilities.
This type of AI, still largely theoretical, would have the ability to think abstractly, understand complex concepts, learn from limited data, and apply its learning to entirely new scenarios. The key distinction of General AI lies in its versatility and adaptability; it’s not confined to the patterns and data it was specifically trained on. Instead, it would possess the kind of general problem-solving skills and understanding that humans use to navigate a wide array of daily challenges.
The development of General AI involves not only advancing computational and algorithmic capabilities but also entails a deeper understanding of human cognition and intelligence. Achieving General AI would mean creating machines that can genuinely innovate, comprehend moral and ethical considerations, and interact with the world in a way that is currently unique to humans.
Currently, this form of AI is more a subject of science fiction and theoretical research than practical application. The challenges in creating General AI are immense, requiring breakthroughs in how machines process information, understand context, and learn autonomously. The pursuit of General AI continues to drive fundamental research in AI, cognitive science, and related fields, pushing the boundaries of what machines might eventually achieve.
Machine Learning (ML) is a crucial aspect of AI that focuses on developing algorithms for computers to learn from data and make decisions. Unlike traditional programming, ML enables systems to identify patterns and improve decision-making with minimal human guidance, adapting over time as they process more data.
ML’s methods include supervised learning (training on labeled data), unsupervised learning (finding patterns in unlabeled data), and reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error). These techniques are applied in various domains, from speech recognition to predictive analytics, making ML versatile in handling large-scale data analysis.
A key strength of ML is its ability to process and interpret vast amounts of data more efficiently than humans. However, the quality of outcomes heavily depends on the data quality; biases in training data can lead to skewed results.
In essence, ML is reshaping data analysis and decision-making, continually advancing the frontiers of AI and its practical applications.
Deep Learning, a subset of Machine Learning (ML), stands out for its ability to process and interpret complex data structures, making it a pivotal technology in the realm of AI. This approach is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, particularly neural networks, and is adept at handling high-level abstractions in data.
Deep Learning utilizes layered neural networks, where each layer processes an aspect of the input data and passes it to the next layer for further refinement. This hierarchical approach enables deep learning models to handle large and complex datasets with a high degree of accuracy and sophistication. It’s especially effective in tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous vehicle navigation.
One of the key advantages of Deep Learning is its ability to learn and improve autonomously as it processes more data. This makes it incredibly efficient for tasks involving large amounts of unstructured data, where traditional ML techniques might struggle.
The success of Deep Learning is heavily reliant on the availability of large datasets and substantial computational power. The more data the system can train on, the more accurate and nuanced its learning and predictions become.
Deep Learning represents a significant leap in the capabilities of AI systems, offering unparalleled efficiency in processing complex, unstructured data. Its ongoing development continues to drive major advancements in various AI applications, pushing the boundaries of what machines can learn and achieve.
Section 2: The Evolution of AI: Focus on LLMs and Beyond
For more than a year, the field of AI has witnessed remarkable growth and evolution, particularly in the domain of Large Language Models (LLMs). These advancements have significantly accelerated the adoption of AI technologies across various sectors.
Rapid Adoption and Expansion of LLMs:
The adoption rate of AI, especially LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT series, has been staggering. For instance, ChatGPT, has seen a meteoric rise in its user base to over 180 million users. In December 2023, ChatGPT had 1.6 billion site visits.
This rapid adoption is reflective of a broader trend where businesses and consumers are increasingly relying on AI for various applications, from customer service to content creation.
Statistics also reveal the burgeoning impact of AI. For instance, AI-driven business solutions have seen a surge in adoption, with significant percentages of companies reporting increased efficiency and cost savings. The number of AI startups and investments in AI research and development have grown exponentially, indicating a robust and thriving ecosystem.

Leading Companies in AI Development:
In the dynamic realm of technology, major companies like Google, OpenAI, Amazon, Salesforce, and Anthropic are not merely utilizing AI; they are actively forging its evolution, embedding AI into their foundational strategies and everyday functionalities in diverse and profound ways.
Google, a titan in the digital world, has seamlessly integrated AI across its myriad services. From refining search algorithms to pioneering AI-driven innovations through DeepMind, Google harnesses AI to enhance user interactions and solve complex problems. Its AI efforts span from the practicality of Google Assistant in facilitating daily tasks to the sophistication of DeepMind tackling global challenges in health and science. These models, known for their remarkable ability to understand and generate human language, have found widespread applications in various sectors, revolutionizing how machines comprehend and interact using natural language.
Amazon’s approach to AI is as vast as its business scope, integrating AI into its e-commerce platform, cloud computing services, and logistics. The omnipresent Alexa and the Echo ecosystem symbolize AI’s infiltration into home life, while Amazon Web Services (AWS) democratizes AI tools and machine learning capabilities for a diverse range of clients. In the realm of logistics and supply chain, Amazon Robotics epitomizes the efficiency and scalability brought by AI in automating and streamlining operations.
Salesforce, a leader in customer relationship management, has infused AI into its CRM systems with Einstein AI. This integration allows businesses to transform customer data into actionable insights, tailoring customer experiences, and automating responses to enhance service efficiency and decision-making. In contrast, Anthropic takes a more focused approach, concentrating on the development of AI that is interpretable and aligns with human values. Their work in AI safety and ethics is a testament to the growing need for responsible AI development, ensuring the technology’s benefits are harnessed without adverse societal impacts.
Parallel to these developments, NVIDIA has emerged as an indispensable player in the AI field, primarily through its GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). Originally designed for graphics rendering in video games, these GPUs are now integral to AI and deep learning, offering unmatched efficiency in processing the enormous datasets required for training complex models. NVIDIA’s contributions extend beyond hardware; they provide a comprehensive ecosystem of software tools, libraries, and frameworks that facilitate AI development and deployment. Their AI-specific technologies like CUDA and specialized hardware like the Tesla and T4 GPUs are specifically tailored for deep learning applications. Moreover, NVIDIA’s Deep Learning Institute plays a crucial role in educating and equipping developers and researchers in the field of AI.
In essence, these companies, each in its unique way, are not just utilizing AI but are actively shaping the trajectory of AI development. Their diverse applications of AI, ranging from enhancing user experiences to addressing ethical concerns in AI development, reflect the multifaceted impact of AI technology in the modern world. As AI continues to evolve, the contributions of these companies are set to define the future landscape of technology and its interaction with society at large.
Section 3: The Advent of Multi-Modal AI
The advent of multi-modal AI represents a significant leap in the field of AI, moving beyond the capabilities of traditional LLMs which primarily focus on text-based processing. Multi-modal AI systems are capable of understanding, interpreting, and generating outputs based on multiple forms of data, such as images, videos, audio, and text. This integration of diverse data types enables AI to achieve a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the world, akin to human perception.
Multi-modal AI’s major innovation lies in its ability to process and synthesize information from various sensory inputs simultaneously. Unlike LLMs that are restricted to text and linguistic patterns, multi-modal systems can analyze visual elements in images and videos, understand spoken language in audio, and even combine these with textual analysis to provide a richer, more context-aware interpretation. This advancement marks a shift towards creating AI systems that can interact with the world in a more holistic and human-like manner.
One significant application of multi-modal AI is in the realm of content analysis and generation. For instance, such systems can analyze a video, not just by its spoken or written content but by understanding the visual context, facial expressions, and even the tone and emotion in the speech. This capability opens new possibilities in fields like media and entertainment, where AI can create more engaging and personalized content, understand audience reactions more deeply, and even aid in content moderation by comprehensively analyzing the multimedia content.
In December 2023, Google’s launch of Gemini marked a noteworthy development in this field. While there has been some controversy regarding the extent of Gemini’s capabilities, it is reported to analyze images, videos, and audio, identifying not just concrete objects but also abstract and semi-abstract elements. Such capabilities of Gemini, if fully realized, could revolutionize how AI systems interact with and interpret complex multimedia content. The ability to understand abstract imagery, a notably challenging area for AI due to the subjective and nuanced nature of such content, signifies a substantial advancement in the AI’s cognitive abilities.
The implications of multi-modal AI like Gemini for users are vast. It can enhance user experience in digital platforms by providing more accurate and context-rich interactions. In education, it can offer immersive learning experiences by understanding and responding to both verbal and visual cues. For businesses, it can provide deeper insights into consumer behavior by analyzing a range of data types, leading to more effective marketing strategies. Moreover, in areas like accessibility, multi-modal AI can aid in creating more inclusive technologies that cater to diverse user needs, interpreting and responding to multiple forms of communication.
Multi-modal AI, exemplified by developments like Google’s Gemini, signifies a major innovation in the AI landscape. By transcending the limitations of traditional LLMs and embracing a more integrated approach to data analysis, multi-modal AI is poised to redefine the interaction between machines and the multi-sensory world, offering enriched applications and experiences for users across various domains.
Section 4: Parallels with Historical Periods of Innovations
The advent of AI, much like historical innovations such as the printing press, the Industrial Revolution, and the digital era, has ushered in a mix of optimism and concern. A report by Goldman Sachs suggests AI could replace up to 300 million full-time jobs, transforming a quarter of work tasks in the US and Europe. However, it also hints at the emergence of new jobs and a productivity boom, potentially increasing global goods and services’ value by 7%.
Generative AI, particularly adept at creating content akin to human work, is at the forefront of this wave. The UK government, recognizing AI’s potential to drive productivity, aims to ensure AI complements rather than disrupts work, and London, U.K. as the second largest AI hub in the world behind San Fransisco, has the potential to shape such outcomes. This sentiment echoes through various sectors. In legal and administrative professions, up to 46% of tasks could be automated, while only a minor percentage in sectors like construction and maintenance face this possibility. Nevertheless, concerns linger, especially in creative fields like art and journalism, where AI’s capabilities might lead to increased competition and wage pressures.
Historically, technological advancements have always been met with a dichotomy of perspectives. While some herald them as harbingers of progress, others caution against their potential for negative disruptions, such as job loss or societal upheaval. AI, too, is viewed through this lens, with some fearing it could contribute to the end of humanity. However, this is a perspective Rise Up Strategies considers unlikely. Instead, the belief is that AI will be a net positive for humanity, possibly our saving grace amidst growing complexities.
For example, Kristalina Georgieva’s analysis for the IMF highlights that almost 40% of global employment could be impacted by AI. While it may replace some jobs, it’s also likely to complement human work, especially in advanced economies where about 60% of jobs might be influenced by AI. The effects within countries could vary, potentially exacerbating income and wealth inequalities. Yet, there’s potential for AI to help less experienced workers enhance productivity more quickly, benefiting younger workers.
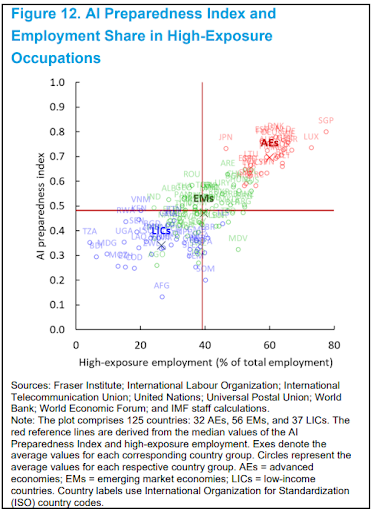
In response to these challenges, comprehensive social safety nets and retraining programs are vital to make the AI transition more inclusive and equitable. The IMF’s AI Preparedness Index underscores the need for readiness in areas like digital infrastructure and regulation. Countries like Singapore, the United States, and Denmark are leading in AI readiness, showcasing the importance of investment in digital infrastructure and workforce competence.
As we embark on this AI era, the emphasis should be on balancing innovation with robust regulatory frameworks and investing in human capital. The AI revolution, much like the printing press or the internet, brings with it challenges and opportunities. It’s a catalyst for change, with the potential to revolutionize medicine, engineering, and various other fields. Embracing AI with a measured approach, focusing on its potential to enhance human capabilities and address complex global issues, is key. The optimism lies in AI’s potential to invent new medicines and engineering solutions, paving the way for a future where technology and humanity coalesce to overcome the challenges we face.
Section 5: AI and Its Economic Impact
The current rush towards understanding and integrating AI in businesses is reminiscent of the fervor witnessed during the digital boom. Today, companies, irrespective of their size, are acutely aware of AI’s disruptive potential and are seeking expertise at a premium, with AI specialists commanding fees of $10k-$15k per day. This scenario echoes the digital transformation era when companies strived to adapt to digital-first models, a shift that was costly for many and led to the obsolescence of those who failed to adapt. In this new era of AI, the transformation is expected to unfold at an even more rapid pace, heralding the emergence of “AI natives.”
The Accelerated Pace of AI Adoption
AI’s impact is profound and far-reaching. Its efficiency and capabilities mean that tasks and processes that once took a team of 100 might now be achievable by a team of 10, revolutionizing timeframes and budgets across all sectors. For instance, tasks that took years can now be accomplished in months, and infrastructure costs can be significantly reduced by leveraging cloud-based AI solutions. This accelerated transformation is poised to redefine the landscape of industries, investing, and venture capitalism.
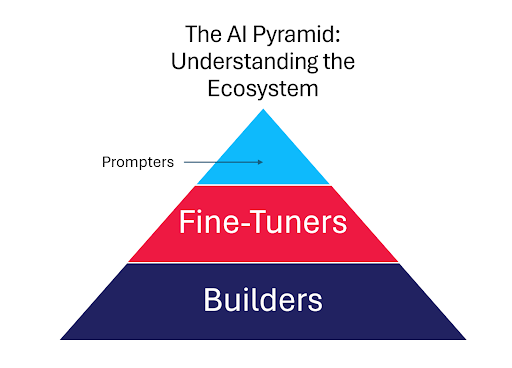
The AI Pyramid: Understanding the Ecosystem
The AI ecosystem can be visualized as a pyramid consisting of three distinct layers, each representing a different type of player in the AI market:
The Builders:
At the base are the Builders, large companies creating the foundational elements of AI. These include firms like NVIDIA, OpenAI and Google, who are at the forefront of developing advanced AI technologies like GPT models and TensorFlow. They are the backbone of the AI revolution, providing the core technologies and platforms upon which other innovations are built.
The Fine-Tuners:
The middle layer consists of the Fine-Tuners. These emerging companies are integrating AI into existing systems, tailoring and enhancing AI capabilities for specific applications. Companies like K Health or Hugging Face, with their AI-optimized GPUs and software, and c3.ai, which provides AI solutions across various industries, exemplify this category. They adapt and refine AI technologies, making them accessible and applicable to a wider range of businesses.
The Prompters:
At the top of the pyramid are the Prompters. These are companies that operate with a low barrier to entry, focusing on creating AI-based applications, tools, and services. They are set to proliferate in the AI market, offering specialized solutions, plugins, and enhancements for existing AI platforms. The anticipated AI stores, like those being developed by OpenAI, will be a marketplace for these innovations, where a multitude of players can offer their AI-driven products and services.
Economic Implications and the Race to AI-First
The race to become AI-first is not just a technological challenge but an economic imperative. Companies that successfully integrate AI into their operations and business models are likely to gain a significant competitive advantage. AI’s potential to drive efficiency, innovation, and scalability is a game-changer, making it a critical factor in future business success.
For industries like healthcare, finance, and retail, the adoption of AI is transforming service delivery, customer engagement, and operational efficiency. In manufacturing, AI-driven automation and predictive maintenance are redefining production processes. The implications for the job market are also significant, with a shift in the skill sets required and the potential for job displacement in certain sectors.
However, the race to AI-first also presents opportunities for job creation in new domains and the evolution of existing roles. The demand for AI specialists, data scientists, and professionals adept at working alongside AI is on the rise. Moreover, AI’s ability to enhance human capabilities can lead to the development of new products, services, and even industries.
Case Study: AI’s Impact in Medicine
Recent advancements in AI have revolutionized the field of drug discovery. A notable example is the Therapeutics Data Commons platform, spearheaded by a team at Harvard Medical School. This initiative aims to enhance the drug development process using AI algorithms to analyze vast biochemical data sets, thereby accelerating the discovery of new medicines.
The process of discovering new drugs is complex, time-consuming, and costly, often taking up to 16 years and billions of dollars. AI addresses these challenges by efficiently analyzing the immense chemical space, identifying potential compounds for medicinal use much faster than traditional methods.
The Therapeutics Data Commons platform serves as a collaborative hub, uniting machine learning researchers and biomedical experts. It facilitates the development of more realistic data sets and algorithms, significantly enhancing the accuracy and speed of identifying new drug candidates.
This approach has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by bringing new treatments to market more rapidly, particularly for chronic and infectious diseases. It demonstrates AI’s transformative impact on healthcare, offering hope for faster, more effective cures.
As organizations navigate this AI revolution, understanding the AI Pyramid and where they fit within this ecosystem is crucial. Embracing AI is no longer an option but a necessity to thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive global market. With AI’s potential to invent new medicines, engineer advanced solutions, and drive economic growth, the future holds promise for those who adeptly harness its power. In this transformative era, AI stands not just as a technological marvel but as a catalyst for a new epoch of human and economic advancement.
Section 6: Future-Proofing Yourself Against AI Disruption
There is no question that the workplace landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. This shift necessitates that workers not only adapt but also proactively equip themselves with skills and strategies to thrive in an AI-integrated future. Understanding how to navigate this new terrain is crucial for career longevity and success.
The first step in future-proofing oneself against AI disruption lies in skills development. Workers should focus on enhancing their data literacy, as interpreting and analyzing data is becoming a staple in almost every professional job role. Additionally, having a foundational understanding of AI and machine learning, even for those in non-technical positions, is becoming increasingly valuable. This knowledge can range from basic AI concepts and terminology to an understanding of how AI impacts one’s specific industry.
For those who are more technically inclined, acquiring programming skills, particularly in languages favored in AI development like Python, opens up direct pathways to engaging with AI initiatives. However, technical prowess alone is insufficient. The human elements of critical thinking, complex problem-solving, and ethical considerations in AI use remain as vital as ever. AI may excel in processing vast amounts of information, but applying this data to real-world problems and doing so responsibly still relies heavily on human judgment and insight.
Another key aspect of adapting to an AI-driven workplace is the ability to continuously learn and stay abreast of rapid technological advancements. The AI field is dynamic, with new developments and applications emerging regularly. Staying informed and adaptable ensures that one’s skills and knowledge remain relevant.
Beyond individual skill enhancement, aligning with AI-native companies – those that are not just using AI but are at the forefront of building their business models around it – is a strategic move. These companies are likely to be the disruptors of their industries, leading the charge in innovation and new business practices. For high-performing workers, these environments offer not just job security but opportunities to be part of cutting-edge work in AI application and development.
Navigating the AI marketplace requires discernment. Workers should research and observe how potential employers are implementing AI, looking for signs of genuine integration rather than superficial use. A company’s culture, particularly its approach to innovation, continuous learning, and AI ethics, can be indicative of how deeply AI is embedded in its operations. Networking, engaging with industry events, and following thought leadership in AI can provide valuable insights into which companies are leading in AI utilization and how they are doing so.
As the workplace evolves with the integration of AI, workers who are prepared, adaptable, and aligned with innovative companies will not only secure their place in the future job market but also contribute significantly to the evolving narrative of AI in the workplace. This period of transformation, while challenging, also presents unparalleled opportunities for growth, innovation, and the redefinition of work as we know it. The key lies in embracing change, upskilling strategically, and choosing to be part of organizations that are at the forefront of this AI revolution.
Section 7: How non AI-Native Organizations should Adapt
Non AI-native organizations are confronted with the urgent need to adapt to the disruptive force of AI. This adaptation is crucial not only for staying competitive but also for harnessing the transformative potential of AI. For organizations uncertain about navigating this shift, partnering with AI expertise from firms like Rise Up Strategies offers a strategic pathway to effective AI integration.
Understanding the unique impact of AI on a specific business model, policies, processes, and culture is the foundational step in this journey. AI experts from Rise Up Strategies can provide a comprehensive analysis, identifying areas ripe for AI integration and aligning these initiatives with business objectives. Their role is to demystify AI, breaking down what can often seem like an overwhelming technological frontier into practical, actionable strategies.
The process of adapting to AI extends beyond just technological implementation; it involves a holistic transformation of the organization. This is where the principles of effective change management, as outlined in the Change Management module on the Rise Up Strategies website, become critical. Change management is not just about adopting new technologies but preparing, supporting, and helping individuals and teams to navigate and embrace organizational change. By embedding these practices into their strategy, companies can ensure a smoother transition, aligning their workforce with the new AI-driven paradigm.
Internally, companies need to foster a culture of innovation and continuous learning. Encouraging employees to develop new skills relevant to AI and data literacy is vital. This effort should be complemented by evaluating and revising business processes to identify where AI can bring efficiency and improvements, such as automating routine tasks or enhancing data analytics capabilities.
Furthermore, given that AI systems are as good as the data they operate on, establishing robust data management practices is essential. This ensures the availability of high-quality data to fuel AI systems effectively. Equally important is the implementation of ethical AI practices. As AI becomes more integrated into operations, organizations must develop guidelines and policies for responsible and fair AI use.
The transition to AI is not just a technological shift but a comprehensive organizational transformation. By seeking external expertise from AI specialists and embracing change management best practices, non AI-native organizations can navigate this transition effectively. The goal is to evolve not just in technological capabilities but also in mindset, culture, and operational approach. As companies undertake this journey to become AI-augmented, they position themselves for growth, innovation, and success in a future where AI is an integral part of the business landscape.
Section 8: Conclusion
As we journey through “Artificial Intelligence: Navigating the Wave of Innovation,” it becomes increasingly clear that AI is not just a technological novelty but a transformative force reshaping the very fabric of industries, economies, and workplaces. The parallels drawn from historical innovations remind us that while AI brings challenges, it also offers unprecedented opportunities for growth, innovation, and human advancement.
For businesses and workers alike, the AI era demands a proactive approach. Companies, whether AI-native or not, must strategically integrate AI into their business models, policies, and cultures. This is a journey that transcends mere technological adoption; it’s about nurturing a mindset of innovation, adaptability, and continuous learning. For workers, the need to upskill and align with AI-forward organizations is paramount. The skills in data literacy, AI basics, critical thinking, and ethical AI use, coupled with a mindset of lifelong learning, are the keys to thriving in an AI-augmented workplace.
Non AI-native organizations, in particular, face the critical task of adapting to this new era. Seeking expertise from AI specialists like those at Rise Up Strategies can provide the guidance and insight needed to navigate this transition. As outlined in the Change Management module on the Rise Up Strategies website, effective change management practices are essential for a smooth transformation. These practices, along with internal efforts to foster a culture of innovation and ethical AI use, will ensure that organizations do not just survive but thrive in the AI era.
The race to AI-first in the business world mirrors the urgency and excitement once seen during the digital boom. The AI Pyramid – with Builders, Fine-Tuners, and Prompters – illustrates the diverse ecosystem of AI innovation. Companies must understand where they fit in this landscape and how they can leverage AI to enhance their operations, services, and products.
As AI continues to evolve and redefine what is possible, embracing it with strategic intent and ethical consideration is imperative. AI holds the potential to unlock new frontiers in medicine, engineering, and beyond, promising a future where technology and humanity synergistically address the complexities and challenges of our time. For organizations looking to be part of this transformative journey, partnering with AI experts like Rise Up Strategies is a crucial step towards becoming AI-native and harnessing the power of AI for a prosperous and innovative future.